Last updated by: RichardWhellum, Last updated on: 09/05/2025
How to Use MinIO
Document Creation: 22 September, 2024. Last Edited: 29 April, 2025. Authors: kghdxx, Jesse Rees, nouri-devv.
Document Code: ONB3. Effective Date: 22 September 2024. Expiry Date: 29 April 2026.
MinIO is the object storage for data warehouse.
MinIO stores files in buckets that can be accessed with the combination of MinIO created 'Access Keys' and 'Secret Keys'. These work similar to AWS S3 storage and can be used with other software downstream as if it was AWS S3.
MinIO serves as a set of folders that use the VM's storage and can be accessed through credentials to upload/download data. Making it more user friendly than storing files on the VM directory alone.
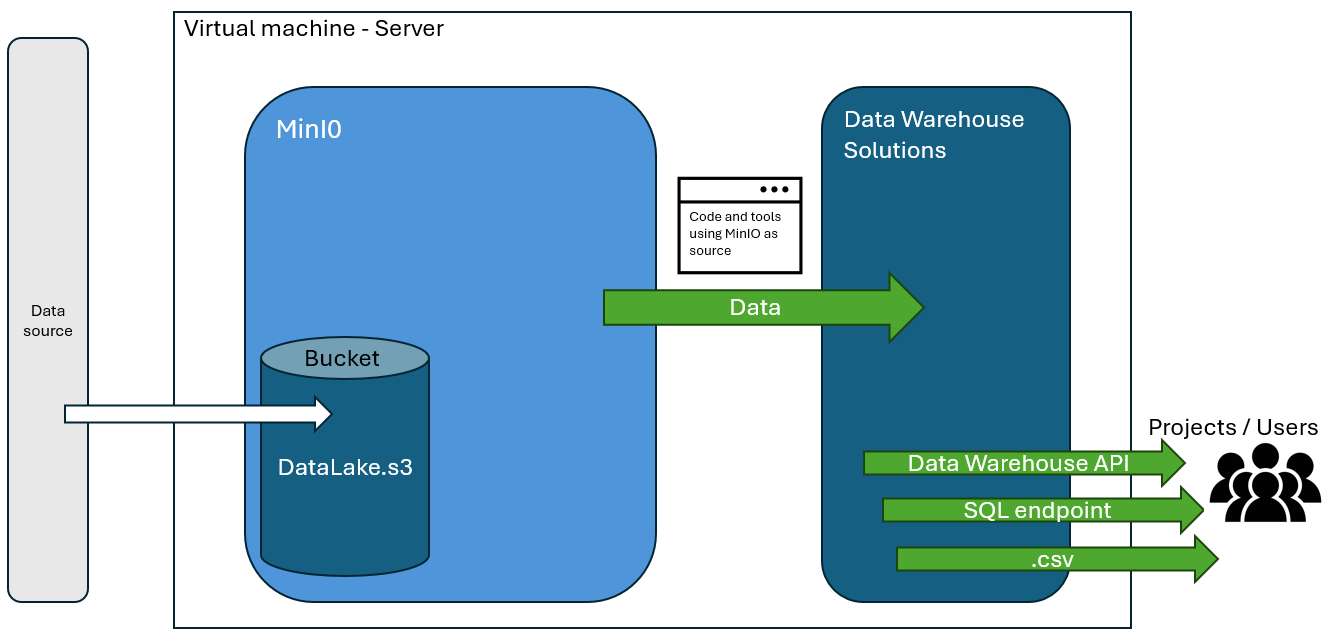
At the time of writing MinIO is located on port 9000 and is accessed by a number of other Data Warehouse tools it's recommended this port isn't modified unless absolutely necessary as it will break tools downstream.
To access existing MinIO data
- Using the GUI
Accessing the MinIO object store through the GUI will first require entering the username and password. This is not included in this text for obvious security reasons but can be retrieved from the Data Warehouse mentor or current Data Warehouse leader.
Once authenticated the user will be presented with a MinIO object store user-interface.
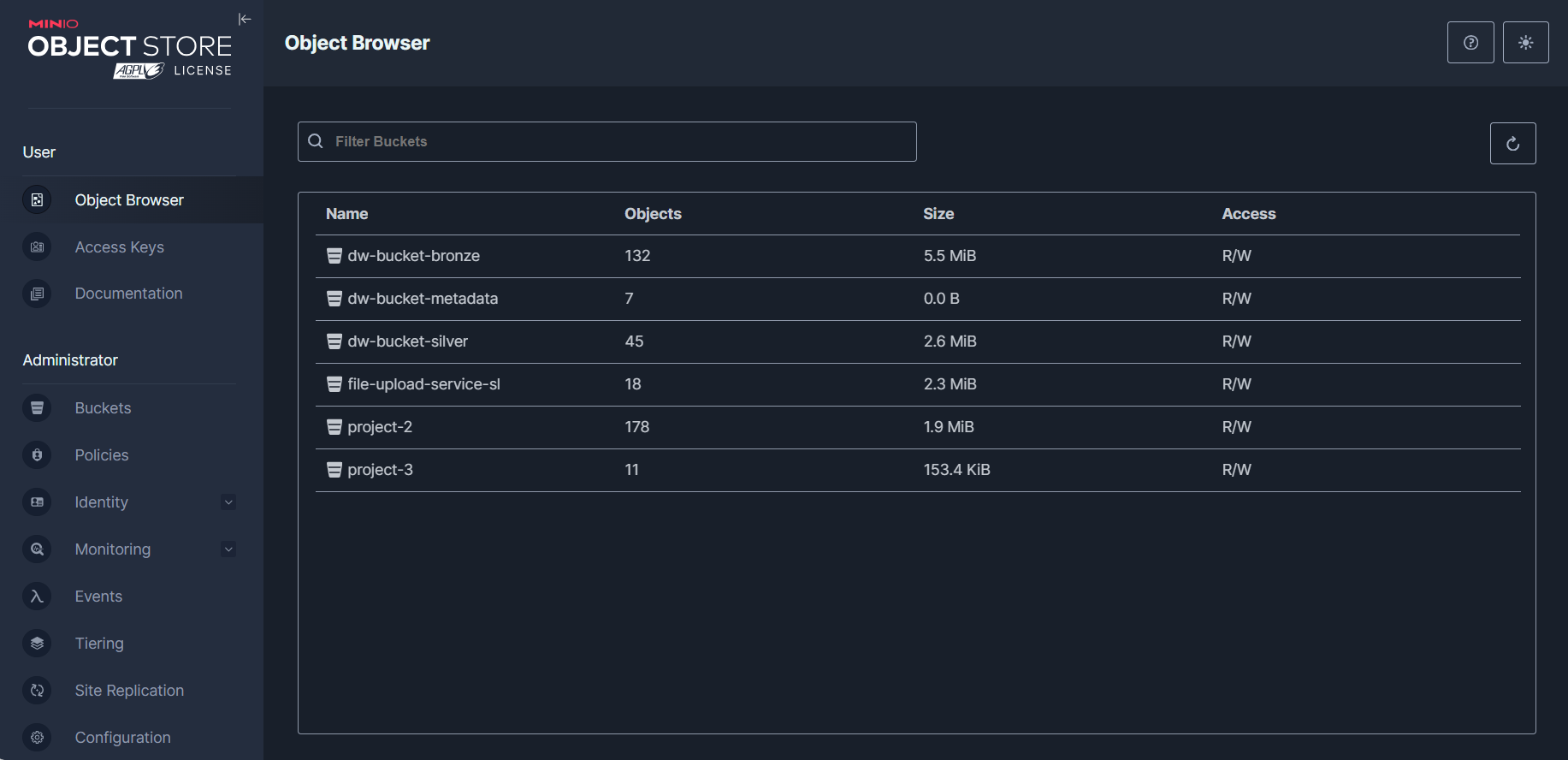
As mentioned above MinIO stores files in 'buckets' to accommodate for different file types (flat, semi-structured and object).
There are already buckets that exist in the MinIO server on the virtual machine including 'dw-bronze-bucket' and 'dw-silver-bucket'. These are sources of the Redback File Upload System.
For the purposes of inspection following the MinIO address in browser will offer a GUI where navigation of buckets and files is possible as well as creation of credentials. This makes it easy to keep track of where files are being sent to and what path they can be accessed from as well as deleting and other admin tasks.
- Using code
This is the most suitable way for data warehouse to utilise the MinIO object store.
Any code or file that needs to access files from MinIO or aims to upload files to MinIO requires an Access Key and Secret Key as mentioned above. It's recommended that these are stored in environment variables (.env file) and then excluded using a .gitignore file. Redback security policies won't allow for files with hardcoded credentials to be uploaded to GitHub.
An example code block to access a file from MinIO:
(referencing environment variables from a .env file)
get env ()
access_key = AWS_ACCESS_KEY
secret_key = AWS_SECRET_KEY